Microbiology 13 - Opportunistic viral infection Flashcards
(41 cards)
What is the Baltimore classification?
Virus classification system
What class of viruses form latent infections?
DNA viruses
What do IgM and IgG differentiate?
IgM = active or resolving infection
IgG = past infection >6wks ago
How is most viral serology performed?
Indirectc ELISA
immune response to virus
tests if you have ever had infection - measures Ab levels
What is the marker of replication and immune response in Hep A?
replication = HAV in stool
immune response - anti-HAV IgM 4-18w

What is the marker of replication and immune response in Hep B?
HBsAg
anti HBc IgM starts 12wks → 3-6 months

How can you test whether you have infection CURRENTLY?
direct detection - PCR/viral proteins (LFT/Ag test)
Why can’t you use serology in immunocompromised, and what is used instead?
cannot use serology as immune system is non functional
- screen prior to immunosuppression
- monitor using PCR
Recall 3 reasons for immunosuppression
- Solid organ transplant
- Human stem cell transplant (short term, or long term if they have significant GVHD)
- HIV/AIDS
Recall 4 types of immunosuppressing drugs
- Steroids
- Calcineurin inhibitors
- Anti-proliferative agent (eg. Azothioprine/ mycophenolate)
- Antibodies
What is the most significant immunosuppressive risk factor for opportunistic viral infection?
ASCT

How would you manage HSV 1+2 in immunocompromised?
test HSV IgG prior to immunosuppression
What is a common re-activator of latent HSV?
Stressful situations
How can VZV manifest?
pneumonitis
encephalitis
hepatitis
purpura fulminans in neonate
shingles
multi dermatomal/disseminated
late presenting
What is the treatment for VZV in the immunocompromised?
varicella - antivral for 7-10 days
zoster - antiviral (IV if disseminated) and analgeisa
Ramsey Hunt - + steroids
HZO - topical steroids
What is the most common malignancy caused by EBV?
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
Latent infected B cells have polyclonal activation → predispose to lymphoma
Suspicion on rising EBV viral load (>10^5c/mL) and CT scan
confirm on biopsy of LN
Management of PTLD
Reduce immunosuppression
Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (Rituximab) - removes B cells
What is the most important opportunistic virus in transplant patients?
CMV
causes allograft disease + GIT (e.g. renal)
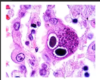
What is the Pathognomonic histological feature of CMV?
Owl’s eye lung pneumocytes (inclusion bodies)
What drug would you give to someone who has CMV AND is immunosuppressed?
ganciclovir (IV) = BM suppression
valganciclovir (oral)
foscarnet (IV) - nephrotoxicity!
cidofovir - nephrotoxicity
IVIg with another drug for pneumonitis
reduce immunosuppression
In renal transplants, is risk of CMV transmission when the donor or recipient is positive?
Donor is pos
immunosuppressed pt gets given some CMV for first time
In Human Stem Cell Transplants, is risk of CMV transmission when the donor or recipient is positive?
Donor is neg (recipient is pos) as patient with CMV has immune system replaced with one that is CMV-naive
How to prevent CMV post transplant?

What CMV prophylaxis is offered, and to whom?
Ganciclovir
Given to all transplant patients






