Chemical Pathology 2 - Lipoprotein metabolism, CVD and obesity Flashcards
(49 cards)
How is cholesterol transported in the fasting plasma?
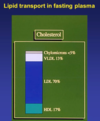
What are the sources of cholesterol
Diet and bile
Where is cholesterol and bile resorbed?
Cholesterol - jejunum
Bile acids - terminal ileum
What is the role of HDL?
Picks up excess cholesterol from the periphery and transports it to liver
What controls the amount of cholesterol resorbed into the intestine?
Balance of 2 enzymes: NPC1L1 and ABC G5/G8
NPC1L1: out of jejunum (to enterocyte?)
ABC G5 and G8: cholesterol into jejunum
How is cholesterol synthesised in the liver, and what is it downregulated by?
HMG CoA reductase
Gut resorption of cholesterol
Which enzyme converts cholesterol to cholesteryl ester?
ACAT
also makes VLDL
add MTP enzyme with apoB TG
What is the function of 7-alpha hydroxase in cholesterol metabolism?
Which enzyme converts cholesterol to bile acids
Which enzyme converts cholesterol to bile acids
What is the function of 7-alpha hydroxase in cholesterol metabolism?
How is Cholesterol-ester taken up in the liver?
SR-B1
What is the role of the enzyme CETP in cholesterol metabolism?
HDL to VLDL conversion
VLDL → TG → HDL
HDL → cholesterol-ester → VLDL
How is LDL taken up in the liver?
LDL receptor
What is the function of LDL vs HDL
LDL cholesterol from liver to periphery
HDL cholesterol from periphery to liver with ABC A1
What is VLDL constituted of?
ApoB, cholesteryl ester and triglyceride
What is the main component of mixed micelles?
Bile acids
Where are bile acids resorbed?
Terminal ileum
How are triglycerides transported in the fasting plasma?

What is the main source of triglycerides?
Diet and small intestine
REcall the steps in triglyceride metabolism
- Broken down into fatty acids then resynthesised into triglycerides
- Transported via chylomicrons into plasma
- Chylomicrons hydrolysed in plasma into free fatty acids using lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
- FFAs taken up by liver and adipose tissue
- Liver resynthesises FFAs into triglyerides
- Exported as VLDL → LPL → FFA
What is the inheritance pattern of familial hypercholesterolaemia type II?
Heterozygous dominant
What mutations are present in familial hypercholesterolaemia (type2)?
LDL receptor
apoB
PCSK9 gene
RARE: LDLRAP1, autosomal recessive
Which mutations are present in polygenic hypercholesterolaemia?
NPC1L1
HMGCR
CYP7A1
What name is given to an inherited predeliction to high HDL, and what mutation causes this?
Familial hyper alpha lipoproteinaemia
= CETP deficiency
What condition is caused by ABC G5/G8 mutation?
Phytosterolaemia