Microbiology 20 - Neonatal and Childhood infection Flashcards
(31 cards)
What infections are currently screened for in pregnancy in the UK?
Hep B
HIV
Syphilis
What does TORCH stand for?
Toxoplasmosis
Other (syphilis, HIV, Hep B/C)
Rubella
CMV
HSV
What long term effects can toxoplasmosis have on the neonate?
Deafness, low IQ and microcephaly
How can txoplasmosis be transmitted?
cat faeces contain oocysts
oocysts may be ingested if cat pet
What are the clinical features of toxoplasmosis?
4 C’s
- Choroidoretinitis
- Microcephaly/hydrocephalus
- Intracranial calcifications
- Seizures / convulsions
Hepatosplenomegaly/jaundice
Recall the symptoms of congenital rubella syndrome
Classical Triad:
- Cataracts
- Congenital heart disease (PDA; ASD/VSD)
- Deafness/SNHL
Brain pathology
BLUEBERRY MUFFIN RASH
What is the cause of a ‘blueberry muffin rash’ and in which infection is it seen?
Extramedullary haematopoiesis
Congenital rubella syndrome
Recall the symptoms of congenital HSV infection
speads to neonate through genital tract
Nasty disseminated infection, causing:
- Meningoencephalitis
- Ulcers and skin problems
- High mortality
How does chlamydia present in the neonate?
Infection transmitted during delivery
Mother may be asymptomatic
Causes neonatal conjunctivitis or pneumonia (RARE)
How would you treat congenital chlamydia?
erythromycin
What are the ‘big 3’ neonatal infections?
Listeria
E coli
Group B strep
How do neonatal infections present?
bacteraemia
meningitis
sepsis
UTI - E coli
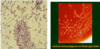
Describe the microbiology for group B streptococcua
gram +ve coccus (purple cocci)
catalase -ve
beta-haemolytic (whiteness around colonies)
Lancefield group B

Describe the microbiology of E. coli
Gram -ve rod

Describe the microbiology of Listeria monocytogenes
Gram +ve rod
What is the treatment for early onset neonatal sepsis
benzylpenicillin (GBS)
gentamicin (E coli)
additional meningitis - amoxicillin (Listeria)
What is the most common cause of late-onset sepsis in neonates?
Coagulase negative staph
What is the first line treatment for late-onset neonatal sepsis?
Cefotaxime (this is brain-penetrative) and vancomycin (this is good for staph)
2nd lin e- meropenem
Community-acquired: cefotaxime, amoxicillin ± gentamicin
What secondary infection is common after chickenpox?
Group A streptococcus
When is lumbar puncture contraindicated in meningitis?
meningococcal, ↑ ICP, bleeding disorder
Describe the CSF characteristics for bacterial viral and fungal/TB meningitis

Describe the microbiology of Neisseria meningitidis
gram -ve coccus
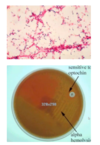
Describe the microbiology of streptococcus pneumoniae
Gram-positive diplococcus, Alpha-haemolytic, Optochin-sensitive (donut colonies)
Describe the microbiology of Haemophilus influenzae
Gram-negative rod, grows glossy colonies on blood agar (needs chocolate agar)



