Histopathology 16 - Neurodegeneration Flashcards
(31 cards)
Recall the pathophysiology of prion disease
transmissible factor
no DNA or RNA - “Prion” Proteinaceous Infections Only
prion protein transmitted - changes host protein into pathological form (beta pleated)
Prion protein cannot be metabolised and accumulates
Recell the clinical features of vCJD
sporadic neuropsychiatric disorder in patients <45 years old
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Dementia
Longer duration than CJD, liked to BSE (Mad Cow Disease)
diagnosed at autopsy
What is histologically characterisitic of prion disease?
Spongiform encepalopathy (tissues are full of vacuoles)
Prion protein deposits

Recall 4 histopatological features of a brain with Alzheimer’s dementia
Extracellular plaques
Neurofibrillary tangles
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Neuronal loss (cerebral atrophy)
How is the APP protein processed in AD?
normal = non-amyloidogenic
cleavage of APP throgh Ab sequence → no Ab protein forms
amyloidogenic
cleavage of APP at transmembrane site → Ab protein
amino terminus of Ab cleaved → too much Ab → Ab thrown out of cell and accumulates → Ab forms monomers, to oligomers (dimers), to protofibrils and then fibrils (polymers)

What are the effects of amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer’s disease?
Ab toxicity more likely intracellular (extracellular plaques probably don’t cause direct problems)
- Ca dysfunction
- ROS through mitochondria
- synaptic dysfunction
- breakdown in proteosome system (more protein buildup →)
- hyper-phosphorylated Tau
What does Tau staining show in Alzheimer’s disease?
intraneuronal hyperphosphorylated Tau - disrupts cytoskeleton of neurones
How is Alzheimer’s disease diagnosed at post-mortem?
Tau staining
What grading is used to stage Alzheimer’s disease at post-mortem? Recall stages.
Braak grading
Stage I = trans-entorhinal region
Stage II = entorhinal region (interfaces neocortex and hippocampus)
Stage III [S] = temporo-occipital gyrus (see the immunostaining by eye)
Stage IV [S] = temporal cortex
Stage V = peri-striatal cortex (cortex around the primary visual cortex)
Stage VI = striatal cortex (occipital lobe)
What is cerebral amyloid angiopathy in AD?
Deposits of proteins in blood vessel walls
Impairs vascular function

Where is neuronal loss and cerebral atrophy most present in AD?
Hippocampus (inf. horn of lat. ventricles often affected) → loss of short-term memory
What is the basic pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease?
loss of dopaminergic cells in substantia nigra
SN → basal ganglia (caudate and putamen) - important in initiation of movement
Lewy bodies/a-synuclein
Describe this finding and explain why it occurs
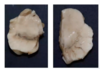
locus classicus
substantia nigra: dopaminergic cells produce neuromelanin → colour
Parkinson’s disease = death of dopaminergic cells of SN → coloration of SN lost
What is the classic triad of symptoms in Parkinson’s disease?
bradykinesia, rigidity, pill-rolling tremor
60-70% of nigral neurones need to be lost before patients become symptomatic
What is the role of Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease?
Lewy bodies = intracellular accumulations of a-synuclein
abhorrent metabolism of a-synuclein – mutations in a-synuclein gene
What is the diagnostic gold standard for Parkinson’s disease?
a-synuclein immunostaining

Recall the Braak stages for Parkinson’s disease
Based on distribution of asynuclein pathology throughout brain
Bottom-up spread: medulla → pons → midbrain (so nigral pathology is only stage III) → basal forebrain → cortices

How does Parkinson’s disease manifest in peripheral ganglia?
gut and nose (i.e. anosmiais an early sign of PD)
<5% aetiology genetic → two potential environmental agent routes
- Retrograde from the gut to the medulla via the vagus nerve
- Through the nose
REcall three examples of Parkinsonism
- Multiple system atrophy
- progressive suprauclear palsy
- corticobasal degeneration
What is multiple system atrophy?
a-synucleinopathy but targets glial cells
affects cerebellum → falls
What are comma shaped inclusions indicative of?

MSA
What is the pathophysiology of progressive supranuclear palsy
Tau - astrocytic and oligodendrocytic
What is the pathophysiology of corticobasal degeneration?
Tau proteinopathy - astrocytic pathology
What are Tau Immunostaining Diseases?
PSP, CBD, Pick’s Disease
Tau mutations → fronto-temporal dementia phenotype often associated with Parkinson’s disease phenotype rather than an Alzheimer’s disease phenotype