Chemical Pathology 23 - Clinical chemistry CPC Flashcards
(32 cards)
what electrolyte imbalance is associated with depression?
hypercalcaemia (Hypocalcaemia → irritability and fits; hypercalcaemia → subtle tiredness, depression)
Ca affects brain and nervous system (before heart muscle)
What does hypokalaemia lead to?
myocardium more irritable → arrythmias → VF
K affects heart before brain and NS
as potassium rises, myocardium becomes more stable, however, ultimate stable rhythm = asystole
What is a Smith’s fracture
posterior displacement of radius (i.e. radius towards BACK of hand)
fall on FLEXED wrist

What is a Colle’s fracture?
anterior displacement of radius (i.e. radius towards PALM of hand)
fall on EXTENDED wrist
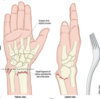
What is a Pott’s fracture?
ankle fracture - both tibia and fibula
What is the likely cause of severe abdo pain with +++ blood on dipstick?
renal stones - tear urothelium → macroscopic
NB glomerulonephritis - microscopic haaematuria
What would urine dipstick show in acute rheumatic fever?
proteinuria (or normal)
What would dipstick show in subacute bacterial endocarditis ?
microemboli, microscopic haematuria, splenomegaly
How would you differentiate calcium stones and gallstones on AXR?
Calcium stones are radio-opaque, but urate stones are radio-lucent
Which test is most important to do first - PTH or Calcium?
do plasma calcium before PTH because you need calcium level to interpret any PTH level
Causes for hypercalcaemia
Cancer (most common inpatient)
Primary HPT (most common community)
Sarcoidosis
High calcium, normal PTH causes
PTH NOT suppressed (inappropriately normal) despite hypercalcaemia → so primary HPT most likely
What are PTH and Ca levels in sarcoidosis?
↑Ca produced -> suppresses PTH
What are PTH and Ca levels in cancer?
↑PTH - endogenous production
from PTHrP or invading bone cancer
Recall the actions of PTH
Kidney
activate 1⍺ hydroxylase → vitD activation
- Absorb calcium and phosphate from gut
- Absorb phosphate from gut
directly resorb calcium
directly excrete phosphate
Bones
activate osteoclasts

features of hypercalcaemia
Moans, bones, groans and stones
Many can be asymptomatic
Polydipsia/polyuria (nephrogenic DI) → calcium acts like glucose to carry water with it via osmosis
What sign of hypercalcaemia might be visible in the eyes?
Band keratopathy (calcium deposition across front of eye)
CHRONIC hypercalcaemia (NOT hypercalcaemia of malignancy)

What would histology of the thyroid gland show in hyperparathyroidism?
LOTS OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY
What would you visualise on bone histology in hyper parathyroidism?
Brown tumours = multinucleate giant cells - activated osteoclasts in bone
long-standing undiagnosed HPT

What might a hand x-ray show in hyperparathyroidism?
often be normal
Later stages may show cystic changes in the radial aspect
(looser zones are in vit D deficiency)
What is the emergency management of hypercalcaemia?
IV access and catheter
FLUIDS - IV 0.9% saline
- 4-hourly or 6-hourly bags of 1L 0.9% NaCl
- 1st bag of 1L given over 1 hour (if severely dehydrated)
IV frusemide
- prevent pulmonary oedema and aid calciuresis
maybe IV pamidronate (bisphosphonate) 30-60mg
- Do not take effect for around a week and is not given in all circumstances
- Hold off to begin with as you can’t measure serum calcium and phosphate if given, unlesss hypercalcaemia due to cancer
What are some complications of hypercalcaemia?
What is the non-urgent treatment for hypoglycaemia hyper parathyroidism ?
Well hydrated
Avoid thiazides (reduce hypercalciuria but increase plasma calcium)
Surgery (parathyroidectomy)
- Technetium Sesta MIBI and USS performed - shows hyperactive parathyroid
- If both tests concordant →whole neck does NOT need to be opened
- If tests not concordant → surgeon needs to view all four glands and take out the largest one
Recurrent infections by which microorganism is seen in renal stones?
Proteus mirabilis



