Microbiology 16 - Fungal infections Flashcards
(48 cards)
What is the main conponent of fungal cell walls?
Chitin
What is the main component of fungal cell membranes?
Ergosterol
What is the reproductive method of yeats?
Budding
Recall 3 examples of yeasts that are clinically important
Candida
Cryptococcus
Histoplasma
What are moulds?
Multicellular hyphae - grow by branching and extension
Give 2 examples of moulds that are clinically important
Dermatophytes
Aspergillus
Which stain is used to detect Candida?
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) stain
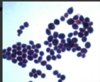
How can different strains of Candida be differentiated
chromogenic agar
Recall the empiric treatment for oral, vulvovaginal and cutaneous candida infection
Topical:
Oral: nystatin
Vulvovaginal and localised cutaneous: co-trimazole
Oral:
Fluconazole
Recall the principles of candidaemia management
- Look for source and signs of dissemination:
- Imaging
- Serology for B-D-glucan
- echo/fundoscopy - Antifungals for at least 2/52 from date of first negative blood culture - repeat BCs every 48 hours (until 2 neg)
Treatment for invasive candidiasis of:
- CNS
- endocarditis
- urinary tract
- bone and joint
- intra-abdominal
- CNS - ambisome/voriconazole
- endocarditis -ambisome/voriconazole
- urinary tract - fluconazole
- bone and joint - ambisome/voriconazole
- intra-abdominal - echocandin/fluconazole
amphotericin B
What does this show

pseudohyphae (germ tube) - only in Candida albicans
What type of agar is used to grow Candida?
selective agar plate impregnated with antibiotics is usually used (Sabouraud agar) → grows in about 48 hours

Waht is Beta-D Glucan assay used for?
look for evidence of invasive Candida infection
Recall the different types of cryptococcus, and which of these infect immunocompetent vs immunocompromised hosts
Serotypes A and D = cryptococcus neoformans (immunocompromised HIV)
Serotypes B and C = cryptococcus gatti (immunocompetent)
Presentation of cryptococcus infection
chronic, subacute to acute pulmonary, meningitis or systemic disease
predilection for CNS (C gatti)
How is cruptococcus transmitted?
Inhalation of aerosolized organisms e.g. pigeons
grows in eucalyptus
What ink can be used to stain for cryptococcus?
India Ink
stain all black except for capsule around yeast (if organism under stress, capsule not always present)
IMPORTANT: Cryptococcal meningitis can cause hydrocephalus which prevents the circulation of CSF so that the sample you take from an LP is not mixing with the CSF in the brain

How to diagnose cryptococcus?
Serum/CSF cryptococcal Ag (CRAG) - used more as quicker + India Ink
How should cryptococcus infection be managed?
- Induction: 2/52 of amphotericin B + flucytosine
- Consolidation: 8/52 of high dose fluconazole
- Maintenance: 1 year low-dose fluconazole
repeat LP for pressure management (hydrocephalus)
pulmonary - fluconazole alone if mild
Which type of aspergillus disease is an allergic disease?
ABPA
can cause spectrum from allergy -> invasive disease
What parts of the body can be infected by aspergillus?
Pre-formed cavities (eg. by TB) - so treated pulmonary TB may be in the history
CXR - RUL cavity with opacity → aspergilloma (post TB)
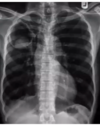
Aspergillosis diagnosis
What is a galactomannan assay used for?
What is a galactomannan assay used for?
Aspergillosis diagnosis