Microbiology 5 - CNS infections and meningitis Flashcards
(34 cards)
What are the four routes of entry into the CNS?
haematogenous spread - most common
direct implantation - via instrumentation
local extension - secondary to established infections e.g. mastoidisits, otitis
PNS → CNS (viral e.g. rabies)
Which antibiotic should be used first line in meningitis?
Ceftriaxone
Is listeria meningitis is suspected, what antibiotic therapy should be used?
Ceftriaxone plus amoxicillin
why is it important to distinguish between meningitis and septicaemia?
IF septicaemia → cannot do LP as can spread
Which pathogen is most likely to be the cause in myelitis?
Poliovirus
What is myelitis?
Inflammation of the spinal cord - disturbance of nerve transmission
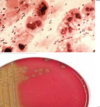
Recall the 3 most likely causative organisms in acute meningitis, and the most susceptible demographic of patient to each
N. meningitidis (gram neg) = young
S. pneumoniae (gram pos) = elderly (so vaccine at 65 years), bimodal
H. influenzae = those who haven’t had HiB vaccine
How is Neisseria menigitidis transmitted?
Person to person, asymptomatic carriers
enters through NP mucosa in susceptible individual
What is the most commonn cause of meningitis in neonates?
Group B strep
normal vaginal colonisation → neonatal scalp microabrasions → transmission
+ Listeria/E Coli
What is the most likely causative organism in chronic meningitis (days to weeks)?
TB - common in immunosuppressed
Cryptococcus neoformans (fungal)
Complications of TB meningitis
Tuberculous granulomas
Tuberculous abscesses (i.e. enhancing thick-walled abscesses)
Cerebritis
What is the most likely causative organism in aseptic meningitis - most common CNS nfection
VIRAL
coxackie
echoviruses
Describe the rash produced by meningococcal meningitis
Non-blanching purpuric rash
What is the most likely viral cause of encephalitis in the UK and worldwide?
UK: HSV
Worldwide: arbovirus
West Nile virus becoming leading cause encephalitis worldwide
Mainly transferred by mosquitoes and birds (European birds spend the winter in Southern Europe and Africa)
Non viral causes of encephalitis
Bacterial
Listeria monocytogenes
Amoeba
direct extension through cribriform plate - Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba & Balamuthia mandrillaris
Habitat – warm water
Toxoplasmosis
obligate intracellular protozoal parasite – Toxoplasma gondii
Recall possible routes of infection that may cause a brain abscess
Direct expansion from otitis media/mastoiditis/paranasal sinusitis
Haematogenous
How would you image brain abscess?
MRI enhancing lesiosn (CT not good at looking at abscesses)
Causes of brain abscesses
(Strep > Staph > gram -ve > other):
Streptococci (anaerobic and aerobic)
Staphylococci
Gram-negative organisms (mainly in neonates)
TB, fungi, parasites, actinomyces and Nocardia species
What is the most common type of spinal vertebral infection?
Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis
spread via
direct open spinal trauma or
spread haematogenously
What is the most common cause of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis?
Infective endocarditis - staph/ strep can be ‘flicked off’ the valve
What is the first investigation to do in suspected meningitis?
Blood cultures
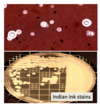
Recall the stains used in CSF analysis to look for a) bacteria b) TB and c) fungi
a) gram stain
b) auramine stain
c) India ink
What is the appearance of CSF in purulent vs aseptic vs TB meningitis?
Purulent: turbid
Aseptic/ TB: slightly turbid or clear
What type of cell is elevated in the CSF in purulent vs aseptic vs TB meningitis?
Purulent: polymorphs
Aseptic/ TB: lymphocytes