Histopathology 16 - Lower GI Flashcards
(55 cards)
what is the aetiology of Hirschprung disease?
absence of ganglion cells of myenteric plexus
→ distal colon fails to dilate
What condition is Hirsprung disease associated with?
Down’s
RET protooncogene Cr10 abnormality
How is Hirschsprung disease diagnosed?
Full thickness biopsy of affected segment - Hypertrophied nerve fibres but NO ganglia
AXR - dilated loop then constricted segment

Treatment for Hirschprung
resection of affected (constricted segment)
What is volvulus?
Complete twisting of bowel loop around mesenteric base, around a vascular pedicle → intestinal obstruction and infarction
which segment does volvulus affect in children and elderly?
children - small bowel
elderly - sigmoid colon
Aetiology of diverticular disease
↑ intraluminal pressure → herniation of bowel mucosa through weak points in bowel wall (usually at points of entry of nutrient vessels)
where do most diverticuli occur?
L colon
Diagnosis of diverticular disease
Barium enema
Endoscopy
Histology

Which drugs cause pseudomembranous colitis?
Abx - cipro/ceph’s kill commensals -> C diff allowed to flourish
Exotoxins -> pseudomembranous colitis
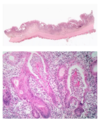
What is this?

wet cornflakes appearance - peusomembranous colitis
Diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis
C diff toxin stool assay
What is this image showing?

volcanic eruption -> pseudomembranous colitis
management for pseudomembranous colitis
metronidazole or vancomycin PO>IV (gut absorption)
NO cipro/cef
Causes of chronic colitis
IBD, TB
Which IBD is more common
UC > Crohn’s
Which part of the bowel is affected in UC?
rectum and colon contiguously
backwash ileitis (terminal ileum also inflamed)
small bowel and proximal GI tract not affected
which layers are affected in UC?
confined to the mucosa
NOT transmural
superficial ulcers
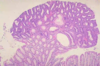
In what condition are pseudoplyps seen?
UC - islands of regenerating mucosa bulge into lumen -> pseudopolyps
How do symptoms differ in IBD?
UC - more bloody diarrhoea
Extra intestinal manifestations of IBD
- Malabsorption and Fe def -> anaemia, stomatitis
- Eyes - uveitis, conjunctivitis
- Skin - erythema nodosum/multiforme, pyoderma gangrenosum, clubbing
- Joints - migratory asymmetrical polyarthropathy of large joints, sacroilitis, myositis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Liver - pericholangitis, PSC (UC>CD), steatosis
Complications of UC
severe haemorrhage
toxic megacolon
adenocarcinoma
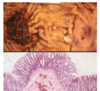
What is this?

UC -> continuous - no skip lesions
What will histology show in UC?
confined to mucosa and inflammtory infiltrate