Histopathology 12 - Respiratory pathology Flashcards
(54 cards)
What are the acute features of the airway in asthma?
Acute bronchospasm
Acute mucosal oedema
Inflammation
What are the chronic features of the airway in asthma?
Muscular hypertrophy
Airway narrowing
Mucus plugging
Define COPD
chronic cough productive of sputum
most days for ≥3 months over ≥2 consecutive years
What are the features of COPD?
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema
How does chronic hypoxia affect the heart?
Pulmonary hypertension —> right heart failure
What is emphysema?
Permanent loss of the alveolar parenchyma distal to the terminal bronchiole
What is the genetic association of emphysema?
Alpha 1 anti-trypsin
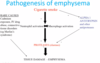
Recall the pathophysiology of emphysema
Smoking causes inflammation
Neutrophil and macrophage involvement
Proteases recruited
Breakdown of epithelium
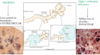
How might histology differ in emphysema caused by smoking vs A1-AT deficiency?
What does lung bullous rupture cause?
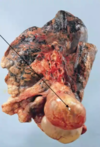
Pneumothorax
What is bronchiectasis?
Permanent abnormal dilatation of bronchi with inflammation and fibrosis into adjacent parenchyma
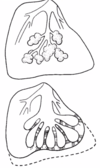
Recall the complications of bronchiectasis
Haemoptysis
Pulmonary HTN
RHF
Amyloidosis secondary to chronic inflammation
What are some inflammatory causes of bronchiecstasis?
- post infectious (children/ CF)
- ciliary dyskinesia [i.e. Kartagener’s syndrome]
- obstruction
- post inflammatory (aspiration)
- secondary to bronchiolar disease (OB) and interstitial fibrosis (CFA, sarcoidosis)
- systemic disease (CTD)
- asthma
Which condition has the strongest association with bronchiectasis?
Cystic fibrosis
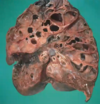
What would you see on histology in bronchiectasis?
massively dilated airways
v little for normal parenchyma gas exchange
filled with mucus and blood
What are the 2 types of causes of pulmonary oedema?
- Leaky capillaries (drugs, inhalation of particles, pancreatitis)
- Back pressure from a failing left ventricle (left heart failure)
What is diffuse alvelolar damage?
acute diffuse lung injury - rapid onset resp failure
includes ARDS and HMD
How does diffuse alveolar damage appear on gross histopath?
Fluffy white infiltrates in all lung fields -“whiteout on all lung fields”
Lungs expanded/firm, plum coloured, airless, often weight >1kg
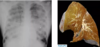
What is hyaline membrane disease?
Insufficient surfactant
Premature babies - HMD of newborn = RDS
What is bronchopneumonia?
Inflammation centred around airway
low virulence
- stapylococcus
- H influenzae
- step
- pneumococcus
Where does bronchopneumonia often affect?
Lower lobes
histopath of bronchopneumonia
patchy bronchial and peribronchial distribution, often lower lobes
peribronchial distribution, acute inflammation surrounding airways and within alveoli

Which type of pneumonia has become much rarer since ABx have been in use?
Lobar pneumonia
High virulence - 90-95% pneumococci (i.e. strep)

Outline the stage of lobar pneumonia
Congestion - Hyperaemia, Intra-alveolar fluid
Red hepatization - Hyperaemia, Intra-alveolar neutrophils (non-atypical)
Grey hepatization - Intra-alveolar connective tissue
Resolution