Histopathology 3 - Breast pathology Flashcards
(57 cards)
What does a triple assessment involve in breast disease?
clinical examination
imaging - sonography, mammogram, MRI (v small lesions that may be missed by US or mammograph
pathology - cytopathology(cells)/histopathology(tissue) - via FNA/core biopsy
Recall the C1-C5 code that is used to grade fine needle aspirate in breast cancer investigation
C1 - Inadequate sample
C2 - Benign
C3 - Atypia, probably benign
C4 - Suspicious of malignancy
C5 - Malignant
What is the gold standard for breast cancer diagnosis?
Histopatholgy
In which type of breast cancer is MRI most useful?
Lobular
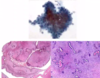
Describe what this image shows. What do the purple stains/pink area/blue arrow show?

terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
- from nipple → branches → end in TDLU
- consist of SNIs and ducts
purple = glandular tissue
pink = stroma
large pink circle = duct with acini around duct
blue arrows = myoepithelial cells - helps pump milk. epithelial (luminal) cells are on inside of myoepithelial cells
define duct ectasia
inflammation and dilatation of large breast ducts
BENIGN
risk factor = smoking
Recall some symptoms of duct ectasia
Pain, mass, nipple inversion and discharge
What would be seen upon cytological analysis of nipple discharge in duct ectasia?
Proteinaceous material and inflammatory cells only
What are some histological features of duct ectasia?
duct distension with proteinaceous material in it
foamy macrophages

What is the most common pathogen identified in acute mastitis?
Staphylcoccal (polymicrobial)
commonly lactational (milk stasis)
What would cytology show in breast mastitis?
neutrophils (acute) - trinucleated dark
and foamy macrophages

How would you treat acute mastitis?
Drainage and Abx
continued expression of milk
What is the cause of fat necrosis of the breast?
Trauma/surgery/radiotherapy
an inflammatory reaction to damaged adipose tissue:
s/s of fat necrosis of the breast
benign painless breast mass
What would you see on cytology in fat necrosis of the breast?
fat cells (empty space) surrounded by macrophages

What is the cause of fibrocystic disease of the breast?
Normal, but exaggerated, response to hormonal influences
causes breast lumpiness (no increased risk Ca)
Histology of fibrocystic disease of the breast
ducts dilated → accumulate stagnant secretions →
ducts calcified (seen on mammogram)

Define fibroadenoma
benign fibroepithelial neoplasm of breast
well circumscribed mobile breast lump
young women; 20-30yo
How can fibroadenoma be cured?
‘Shelling out’
What would you see on FNA cytology in fibroadenoma?
arrows pointing to myoepithlial
glandular epithelial and myoepithelial cells present → benign

What are some histological featuers of fibroadenoma
well circiumscribed edge
compressed glandar component
glandular and stromal cells

Which breast tumours can be described as ‘leaf like’?
Phyllodes tumours
What is a phyllodes tumour?
Potentially aggressive fibroepithelial neoplasm of the breast - but usually benign
How do phyllodes tumours tend to present?
Usually as an enlarging breast mass in women >50 - often in pre-existing fibroadenomas